What are Purlins? How Important are They in Pre-Engineered Buildings (PEBs)?
Every component in a PEB plays an important role in building a strong, reliable, and cost-effective structure. One of the most essential components in the structural framework is the purlin. Though it goes unnoticed to the naked eye, purlins are those unsung heroes that provide strength and stability to a PEB Construction.
In this blog, we will take a closer look at what purlins are, the different types used in construction, and why they are indispensable in the design and performance of pre-engineered buildings.
What are Purlins?
Purlins are horizontal structural members in a roof structure that are laid between the roof ridge and the eaves. They are supported either by rafters or by building walls and serve the primary purpose of supporting the roof deck or sheeting.
In simple terms, purlin are the secondary framing elements placed perpendicular to the main frames (rafters) in a roof structure. They act as a base for roofing sheets and help in transferring loads from the roof to the main frames or columns.
Purlin are crucial secondary structural members in modern pre-engineered buildings. The essential support they offer from the roof covering to the primary structural frame enables the effective use of materials. Modern purlins are made of cold-formed steel; this material offers a weight reduction of around 20-30% compared to the conventional supports made of wood, plus more resistance against corrosion with the aid of galvanizing.
Types of Purlins
The shapes and types of purlin vary, and each serves specific structural needs. In pre-engineered buildings, cold-formed steel purlin’s find extensive applications owing to the lightweight, high strength, and cost-effectiveness they offer. Some common types are:
C-Purlin: Versatile Profile Design
C-purlin have an open C-shaped cross-section that provides a versatile member for roofing and wall applications. Their flange-web geometry provides efficient moment resistance and allows openings in the web for routing utilities such as electrical conduits and plumbing. These purlin normally span between 6 to 9 meters in standard industrial buildings.
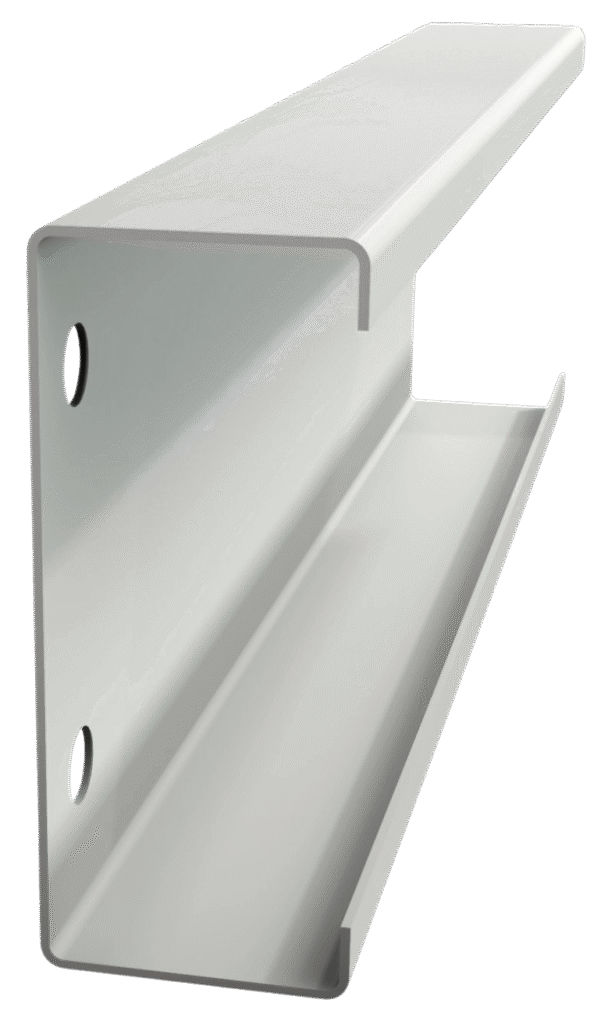

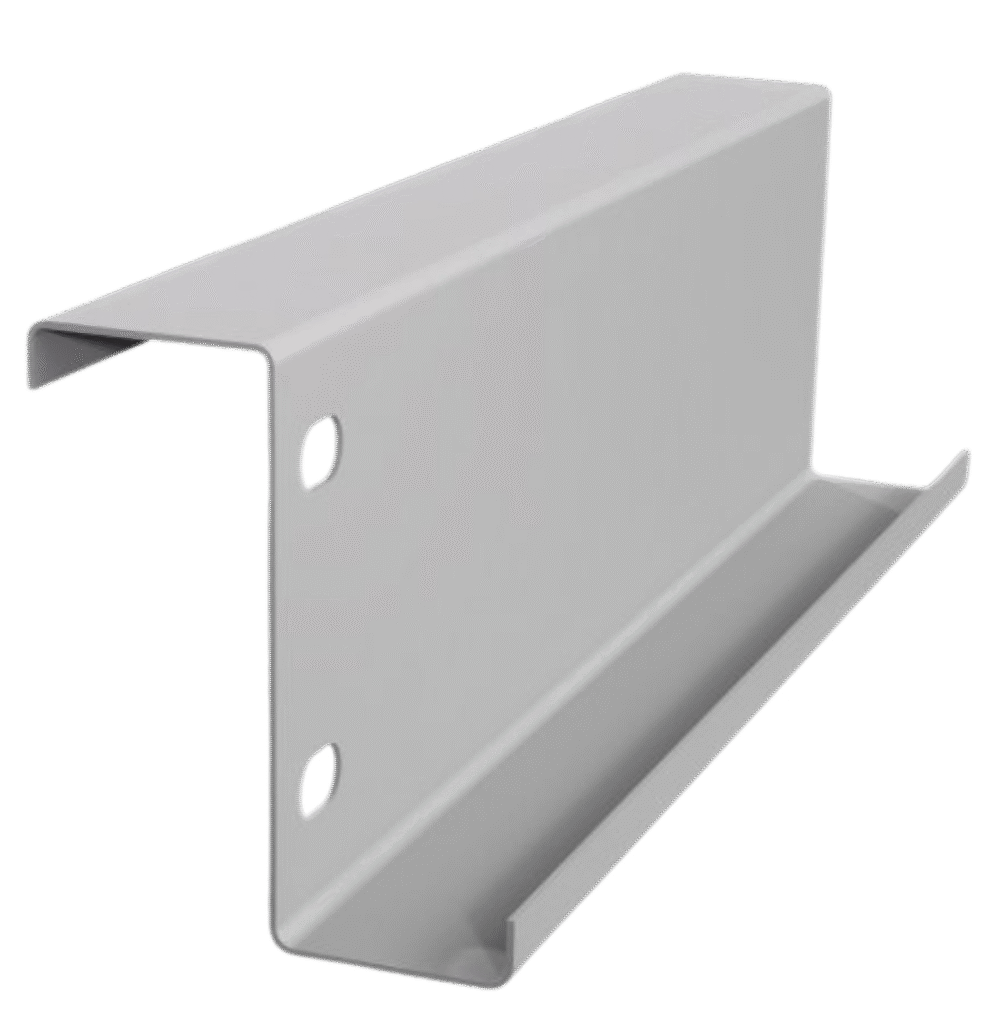
Z-Purlin: Long-Span Optimization
Z-purlin have an asymmetrical Z-shaped section that enables overlap at joints, thereby providing a continuous profile. This greatly enhances load-carrying capability, with spans of over 12 meters easily achievable, thus making it very adaptable for large warehouses and industrial sheds. By using Z-purlin, the requirement of intermediate supports is reduced up to 40% compared to C-purlin.
Materials Used to Manufacture Purlins
- Galvanized Iron (GI): Offers excellent corrosion resistance and durability.
- Mild Steel: Cost-effective and strong, often used with protective coatings.
- Pre-painted Galvalume (PPGL): Provides both structural integrity and aesthetic appeal
Functions and Importance of Purlins in PEBs
1. Structural Support
The purpose of purlin is to support the roof by carrying loads from the roofing sheets and distributing these to the primary frame. Without purlin, the roof will collapse or sag due to self-weight or other external loads such as wind, rain, and snow.
2. Load Distribution
They ensure that both dead loads, such as roofing sheets and insulation, and live loads like wind, snow, and maintenance work, are transmitted efficiently to the major structural elements of the building.
3. Flexibility in Design
The use of different types and sizes of purlin allows engineers to design buildings with varying spans and loading conditions. This flexibility is very important in custom PEB designs where cost and efficiency must be balanced.
4. Lightweight Construction
Cold-formed steel purlin reduce the overall weight of the structure without compromising strength. This not only cuts down on foundation costs but also reduces the construction schedule.
5. Ease of Installation
Purlin are easy to handle, cut, and fix on-site. The standardized shapes and dimensions reduce fabrication time and allow quick assembly, which is an added advantage for the pre-engineered building projects.
6. Cost Efficiency
Purlin lessen material wastage and labor costs since they are manufactured to exact specifications. The usage of high-strength steel further minimizes the amount needed while maintaining safety and performance.
Applications of Purlins in PEBs
- Industrial Warehouses
- Commercial Buildings
- Agricultural Sheds
- Cold Storage Units
- Workshops
- Aircraft Hangars
In each of these applications, purlin play a key role in roofing stability and long-term performance
Difference between Purlin vs. Traditional Wooden Roof Supports
In traditional construction, timber was often used for supporting roofs. However, steel purlins have quickly replaced wood in modern pre-engineered buildings for the following reasons:
| Criteria | Steel Purlins | Wooden Supports |
|---|---|---|
| Strength | High | Moderate |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier |
| Fire Resistance | High | Low |
| Durability | Long-lasting | Susceptible to rot/pests |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable | Deforestation concerns |
| Maintenance | Minimal | Requires treatment |
Conclusion
Purlins may appear insignificant compared to the big picture of a PEB, but they are among the most critical components that ensure the structural integrity, safety, and efficiency of the building. Their role of supporting the roof, distributing loads, and allowing flexibility in design makes them indispensable in any steel building framework.
Whether it is an industrial warehouse or an agricultural shed, high-quality purlin, such as C and Z purlin made of galvanized steel, will significantly enhance the performance and life of your building.

